Microsoft Dynamics AX.
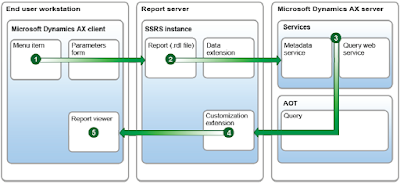
To better understand how a report is rendered, review the following steps.
1. A user requests a report.
Assume that a user clicks a menu item in the Microsoft Dynamics AX
client. The menu item is bound to a SQL Server Reporting Services
report.
After the user clicks the menu item, a parameters form is displayed to the
user. The user enters parameters to filter the data that will be displayed
on the report.
The Microsoft Dynamics AX client then requests the report from
Reporting Services. (The request includes the parameters entered by the user.)
2. Reporting Services receives the request and asks the Microsoft
Dynamics AX server for the report data.
Reporting Services receives the request and examines the report on the
server. The report is stored as an .rdl file. The .rdl file indicates the
report’s data source. (The data source could be a Microsoft Dynamics
AX query, a report data provider class, or an external data source via
report data methods.)
In cases where a Microsoft Dynamics AX data source is used for the
report, Reporting Services will use the Microsoft Dynamics AX data
extension to retrieve the data.
At this point, Reporting Services asks Microsoft Dynamics AX for
metadata about the data source. Reporting Services then requests the data
for the report.
3. The Microsoft Dynamics AX server receives the request and sends
the report data back to Reporting Services.
The Microsoft Dynamics AX services examine the query in the AOT to
return the requested metadata. The services also execute the query to
generate the data for the report.
Microsoft Dynamics AX returns the metadata and data to Reporting Services.
NOTE: Microsoft Dynamics AX enforces security on all data returned. If the
user who is running the report is not allowed to see a specific field, the data for
that field is not returned.
4. Reporting Services renders the report and sends it to the
Microsoft Dynamics AX client.
The Microsoft Dynamics AX customization extension formats the report.
The customization extension uses metadata to provide automatic
formatting of data and can affect the positioning and layout of elements
in the report.
Reporting Services then renders the report into a visual representation
and sends that to the Microsoft Dynamics AX client.
5. The report is displayed to the user.
The Microsoft Dynamics AX client displays the report to the user in the
report viewer control.
Regards,
Hossein Karimi


No comments:
Post a Comment